Focal erosion of the lateral margins secondary to an aneurysm focal erosions of the floor by pituitary lesions and selective erosion of the posteroinferior floor secondary to chronic increased intracranial pressure 3 4 are some of the more dependable findings.
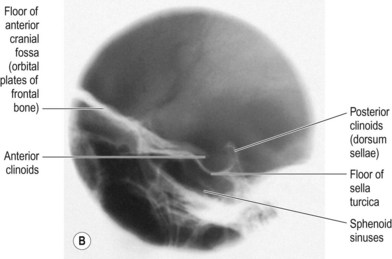
Erosion sellar floor.
Primary or secondary neoplasms including.
Enlargement with erosion of anterior cortex of dorsum sellae proceeds to the floor of the sella and may result in complete destruction of the dorsum.
Furthermore osteolysis of the dorsum sellae and clinoids sometimes occur in childhood leukemia and langerhans cell histiocyto.
Thickening of the tuberculum or of the clinoid processes and blistering of the planum sphenoidale have frequently been reported in association with meningiomas of the sella turcica.
In the sellar type of sinus the thickness of the anterior sellar wall ranged from 0 1 to 0 7 mm mean 0 4 mm compared with 0 3 to 1 5 mm mean 0 7 mm for the presellar type.
Erosion or destruction of the sella turcica can arise with any of numerous intracranial tumors including.
Chordoma of the clivus is frequently associated with erosion of the dorsum sellae and the sellar floor.
Another measurement important in transsphenoidal surgery is the thickness of the anterior sellar wall and sellar floor.
Erosion or remodelling of the pituitary floor is of limited help since it may be a normal finding.
In patients with a known pituitary microadenoma erosion or remodelling of the pituitary floor is a sign of inferior extension.